NA-64 Experiment
Introduction
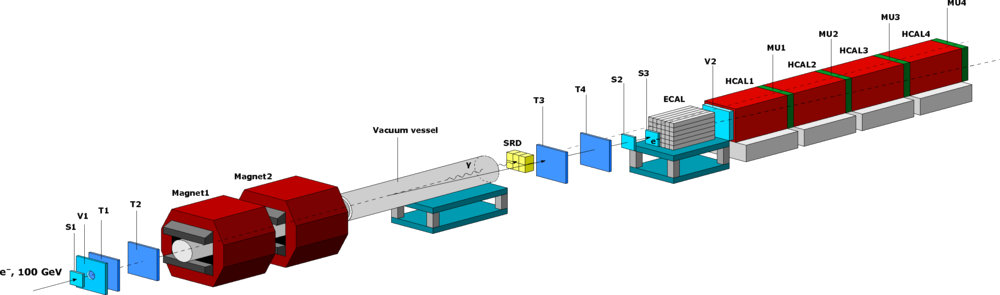
The NA64 experiment (known as P348 at the proposal stage) is a fixed-target experiment at the CERN SPS combining the active beam dump and missing energy techniques to search for rare events. The experiment will build and operate a fully hermetic detector placed on the H4 beam line with the primary goal to search for light dark bosons (Z’) from dark sector that are coupled to photons, e.g. dark photons (A’), or sub-GeV Z’ coupled only to quarks. In some cases the Z’ is coupled only to µ or tau, so we call the Z′ the dark leptonic gauge boson. The experiment is also capable to search for K_L -> invisible decay, which is complementary to K+ -> π+ + ν ν, and invisible decays of π0, η, η′, K_S mesons.
The advantage of our approach is that the sensitivity (or number of signal events) of the experiment is roughly proportional to the Z’ couplig squared ε^2, associated with the Z’ production in the primary interaction in the target. While in a classical beam dump experiment, it is proportional to ε^4, one ε^2 came from the Z’ production, and another ε^2 is either from the probability of Z’ decays or their interactions in a detector located at a large distance from the beam dump. The sensitivities of these two methods depend on the region under study in the (ε^2 ; m_Z’) parameter space, background level for a particular process, available beam intensity, etc. In some cases, much less running time and primary beam intensity are required to observe a signal event with our approach.
The experiment P348 was proposed to the CERN SPSC in January 2014 with the primary goal to search for the A’->invisible and A’->e+e- decay modes. In April 2014 it received recommendations for the test measurements. In January 2016 P348 was recommended for approval as a CERN SPS experiment for the search for the A’->invisible decays. The CERN Research Board officially approved the P348 experiment on March 9, 2016 with the reference number NA64.

The goal of the NA-64 Experiment
This is a fixed-target experiment at the CERN SPS utilizing the active beam dump combined with the missing energy approach for the searches of invisible decays of dark photons (A’) with the mixing strength 10-5 < ε < 10-3and masses MA’ < 100 MeV, invisible decays of (pseudo)scalar mesons, in particular K_S , K_L -> invisible, and hadron and muon interactions resulting in invisible final states due to production of new penetrating particles.
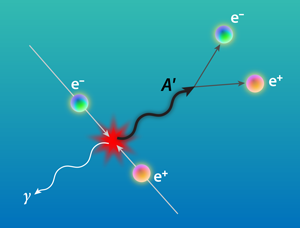
Visible and invisible decays of dark photons
Several models of dark matter suggest the existence of dark sectors consisting of SU(3)C x SU(2)L x U(1)Y singlet fields. These sectors of particles do not interact with the ordinary matter directly but could couple to it via gravity. In addition to gravity, there might be another very weak interaction between the ordinary and dark matter mediated by U'(1) gauge bosons A’ (dark photons) mixing with our photons. In a class of models the corresponding dark gauge bosons could be light and have the γ-A’ coupling strength laying in the experimentally accessible and theoretically interesting region. If such A’ mediators exist, their di-electron decays A’ → e+e- could be searched for in a light-shining-through-a-wall experiment looking for an excess of events with the two-shower signature generated by a single high energy electron in the detector. Our experiment aims to probe the still unexplored area of the mixing strength 10-5 < ε < 10-3 and masses MA’ < 100 MeV by using 50-150 GeV electron beams from the CERN SPS. The experiment can provide complementary coverage of the parameter space, which is intended to be probed by other searches. It has also a capability for a sensitive search for A’s decaying invisibly to dark-sector particles, such as dark matter, which could cover a significant part of the still allowed parameter space. The full running time of the proposed measurements is requested to be up to several months, and it could be taken at different SPS secondary beams.